What are Outstanding Shares? The Motley Fool

This figure is important as it shows the company’s intention to distribute profits, even if the payments have not yet been made. This means the company still owes shareholders USD 500,000 in dividends, which will be listed under current liabilities. This means the company distributes 30% of its earnings as dividends, retaining the remaining 70% for business growth or other purposes.
- The life of common stock goes through a few phases, and understanding each step is important for putting the common-stock-outstanding number into proper perspective.
- In contrast, a higher ratio might suggest that a company prioritises returning profits to shareholders.
- But shares outstanding can tell you important information about the number of shares that a company can possibly sell into the market.
- Generally, both of these figures can be found on a company’s balance sheet.
- Outstanding shares refer to the authorized shares that have been issued to a company’s shareholders, excluding the treasury stock retained by the company itself.
- Armed with this knowledge, investors can make informed decisions, contributing to a robust and strategic investment portfolio.
Related investing topics
- But for mature companies with relatively little movement in share count (either basic or diluted), quarterly and annual data from public sources should easily suffice for solid fundamental analysis.
- These types of investors typically include officers, directors, and company foundations.
- Once you know how to calculate the outstanding shares, you can use this number to calculate a number of valuation metrics, or measures of a company’s performance and future earnings potential.
- Evaluating the trend of this number provides useful insights to investors.
- Understanding a company’s financials is crucial to successful investing.
When a company creates more shares, those shares become part of the shares outstanding. Shares that a company buys back from the open market, reducing the total number of outstanding shares. Changes in shares outstanding over time also reveal how valuable shares are as a stake of ownership in the company, as the number of shares available directly affects this. The float is the portion of outstanding shares that’s most relevant for smaller investors. The first of these, unrestricted shares, is also known as “the float.” These are the shares that can be actively traded on the open market. Let us understand the formula that shall act as the basis of our understanding and the formation of the outstanding shares equation through the discussion below.

Advanced dividend calculations
The quantity of issued shares is approved by the board of directors. Outstanding shares are often confused with float and market capitalisation. To understand the differences between outstanding shares and float, we first need to understand the types of shares. Preferred stock is a special class of shares that is generally considered a hybrid instrument, including properties of both a debt and equity instrument. Preferred stocks are higher ranking than common stock, but also subordinate to bonds in terms of claim, or rights to their share of the company’s assets. From there, scroll down until you find the section in the 10-Q or 10-K called „Capital Stock.“ All the details you need will be there.

Check the Company’s Balance Sheet
- Shares outstanding are the basis of several key financial metrics and can be useful for tracking a company’s operating performance.
- The chart below shows how each is calculated using outstanding shares.
- One possible point of confusion we still need to mention is stock given to employees as compensation, typically in some combination of restricted stock, options, or equity grants.
- Then, add those terms together to get the weighted average number of outstanding shares.
In contrast, outstanding stocks are the ones already issued in the market. Warrants are instruments that give the holder a right to purchase more outstanding stock from the company’s treasury. Whenever warrants are activated, stocks outstanding how to calculate outstanding shares increase while the number of treasury stocks decreases. If all these warrants are activated, XYZ will have to sell 100 shares from its treasury to the warrant holders.
Why shares outstanding matters

The calculation for common stock outstanding can seem a little daunting at first simply because so much accounting jargon is unearned revenue used to define and calculate it. Now that you’re equipped with this foundation of knowledge, all you need to do to figure it out is to go look it up on any company’s balance sheet in their 10-Q or 10-K filing. Explore how corporations authorize and calculate issued shares through market cap and balance sheet methods. It doesn’t mean a company has shares out there laying around or missing.
How to Calculate the Number of Shares of Common Stock Outstanding
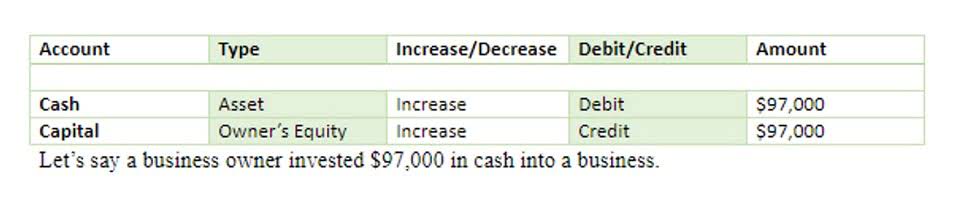
A company’s outstanding shares can fluctuate for a number of reasons. Companies typically issue shares when they raise capital through equity financing or when they exercise employee stock options (ESOs) or other financial instruments. Outstanding shares decrease if the company buys back its shares under a share repurchase program. Dividend calculations provide useful insights into the income potential and financial health of your investments. Also, metrics like dividend yield, payout ratio, and dividends per share allow investors to evaluate returns and assess the sustainability of a company’s dividend strategy. As a stock market beginner, it is important for you to understand key terms related to the share market.
But the number of shares outstanding can be considered good or bad … The more shares a company has, the more the value of the company is spread out. That could be considered bad because each share is worth less of the company. It will also change if the number of shares changes through an offering or stock buyback.
Where to find dividends paid in the cash flow statement
Because the difference between the number of authorized and outstanding shares can be so large, it’s important to realize what they are and which figures the company is using. Different ratios may use the basic number of outstanding shares, while others may use the diluted version. This can affect the numbers significantly and possibly change your attitude toward a particular investment. Furthermore, by identifying the number of restricted shares versus the number of shares in the float, investors can gauge the level of ownership and autonomy that insiders have within the company.
